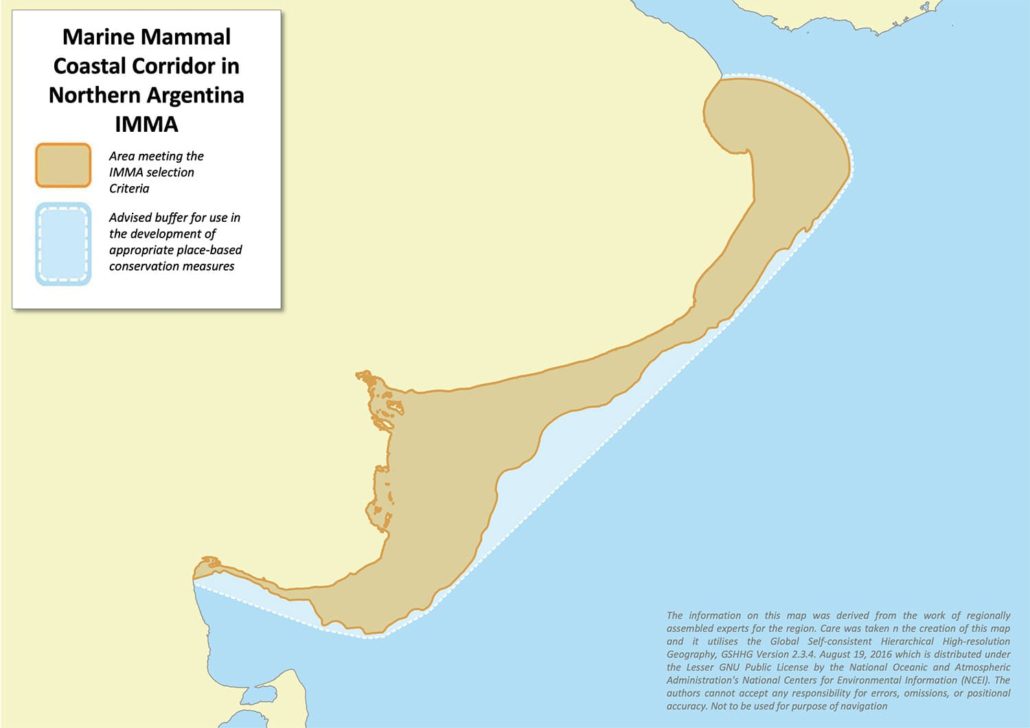
Size in Square Kilometres
93,116
Qualifying Species and Criteria
Franciscana dolphin – Pontoporia blainvillei
Criterion A; B (1); C (1, 2); D (1)
Lahille’s bottlenose dolphin – Tursiops truncatus gephyreus
Criterion A; B (1); C (2)
Southern right whale – Eubalaena australis
Criterion C (3b)
South American sea lion – Otaria byronia
Criterion C (2)
South American fur seal – Arctocephalus australis
Criterion C (2)
Common dolphin – Delphinus delphis
Criterion C (2)
Criterion D (2) – Marine Mammal Diversity
Arctocephalus australis, Delphinus delphis, Eubalaena australis, Megaptera novaeangliae, Otaria byronia, Pontoporia blainvillei, Tursiops truncatus gephyreus, Tursiops truncatus truncatus
Other Marine Mammal Species Documented
Aethalodelphis obscurus, Mirounga leonina, Orcinus orca, Phocoena spinipinnis
Summary
The IMMA encompasses a portion of the coastal continental shelf in northern Argentina’s EEZ. The coastal habitat up to 50m depth is highly productive and serves as important habitat for marine turtles, birds and mammals. The area includes the southernmost distribution of franciscanas (Pontoporia blainvillei) and Lahille’s bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus gephyreus), which are both classified as Vulnerable on both the IUCN and Argentina’s Red Lists. Furthermore, the area hosts genetically differentiated subpopulations of both of these species. The IMMA also hosts six additional species of pinnipeds, small cetaceans and whales. South American sea lions (Otaria byronia) and fur seals (Arctocephalus australis) are present in this area year-round and are functionally connected with populations off Uruguay and Patagonia. The number of southern right whales (Eubalaena australis) using the IMMA is increasing, linking two breeding areas off Brazil and northern Patagonia. An increasing number of records of humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) in the area includes records of entanglement and ship strikes. Coastal and mid-continental shelf fish assemblages (anchovies, sciaenids, squids) are the main prey items for most of the small cetaceans and pinnipeds in the IMMA, and are subject to fisheries pressure. Franciscana dolphins are the species most impacted by bycatch from artisanal fisheries in the Argentine EEZ while common dolphins are more impacted by midwater industrial trawl fisheries.
Description of Qualifying Criteria
Criterion A – Species or Population Vulnerability
The proposed IMMA provides coastal habitat for one Vulnerable dolphin species, the franciscana (Pontoporia blainvillei ; Vulnerable A3d; Zerbini et al., 2017), and one vulnerable subspecies, Lahille’s bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus gephyreus ; Vulnerable D1 ; Vermeulen et al., 2019).
Criterion B – Distribution and Abundance
Sub-criterion B1 – Small and Resident Populations
Lahille´s Bottlenose dolphins were previously reported to be continuous along the coast of Buenos Aires, Río Negro and Chubut provinces off Argentina. However, a considerable reduction in sightings was recorded in the last 20 years, with certain areas where dolphins have almost completely disappeared (Castello et al., 1983; Bastida & Rodríguez 2003; Coscarella et al. 2012; Vermeulen & Bräger 2015; Vermeulen et al. 2018). In the late-1970s to mid-1980s, approximately 100 Lahille’s bottlenose dolphins were estimated to occur in the northern area of the proposed IMMA (San Clemente del Tuyú and Miramar, but a marked decrease in sightings was noted in this area in the late 1980s, after which sightings dropped dramatically in the 1990s despite continued opportunistic survey effort (Bastida and Rodríguez, 2003; Lodi et al., 2016). Furthermore, there are no new coastal areas where the presence of this species has grown substantially over time, ruling out any hypotheses of distribution shifts.
The largest concentration of Lahille’s bottlenose dolphins in this IMMA is Bahía San Antonio and adjacent areas (Río Negro; Svendsen 2013; Vermeulen et al. 2018). The presence of a resident community ranging from Bahía San Antonio to El Cóndor was reported (Vermeulen and Cammareri, 2009; Vermeulen et al., 2016; Failla et al., 2016). Photo-identification studies of Lahille’s bottlenose dolphins in the estuary of Bahía Blanca, conducted between October 2020 and April 2023 showed that bottlenose dolphins were sighted year-round on 30 different occasions, with a cumulative identification of 190 unique individuals. The overall sighting per unit effort (SPUE) was 0.34 dolphin group/hour. Observed group sizes ranged from one to 20 individuals, but most (76.6%) of the groups observed contained between one to eight dolphins (Petracci et al., 2023). The occurrence of bottlenose dolphins in the northern area Bahía Samborombon is low, with few annual sightings of solitary or pairs of dolphins.
Roughly 15% of the Lahille’s bottlenose dolphin groups observed in the Bahia Samborombon contained calves, but never more than one calf per group (Vermeulen et al 2017). Ad hoc observations off Bahía Blanca reported regular sightings of calves. Off San Antonio, up to 72% of the Lahille’s bottlenose dolphin groups encountered contained calves and neonates, and these could be seen throughout the year, suggesting that the shallow waters (<10m) of the bay are used by the dolphins as a calving and nursing area (Vermeulen and Cammareri, 2009). Franciscanas are present year-round in the proposed area (Crespo et al. 2010), and genetic information suggests some site fidelity in females (Mendez et al., 2010). Wells et al (2022) reported that satellite tagged dolphins had relatively small home range sizes, ranging from 132.9 km2 (SD =102.8 km2, range = 51–312 km2, n = 5) in Bahía Samborombon to 463.5 km2 (SD = 344.1, range = 49–1,013, n = 7) in Bahía San Blás. Use of the water column is fairly consistent along its distribution, spending nearly all of their time-at-depth <10 m, and mostly <5 m, with suggested residency over periods of weeks. The latest published franciscana abundance estimates from the area are based on monitoring carried out in 2003 and 2004 , which yielded an estimate of 14,695 individuals for Argentina but excluding Bahía Samborombón (Crespo et al. 2010). The International Whaling Commission’s Scientific Committee is currently coordinating a review of the species and a new abundance estimate is expected to be approved in 2023. The most recent bycatch mortality estimate is between 369-539 animals per year in the proposed area (Negri et al., 2012), a removal that would represent between 2.5-2.7% per year of the population size. It is suggested that removal should not exceed the population growth rate by more than 0.5% (Crespo et al. 2020).
Sub-criterion B2 – Aggregations
Criterion C: Key Life Cycle Activities
Sub-criterion C1 – Reproductive Areas
Stranded (alive and freshly dead) and entangled franciscana calves are documented annually in the southern part of Bahía Samborombon. This suggests the bay is a calving area. The calving period of the franciscana – defined by the period of occurrence of live stranded calves with umbilical cords combined with milk in the stomach – extends over ca. 4 months, from early October to late January, with the highest frequency in November (Denuncio et al., 2013). During an aerial survey performed in March 2022 along the coast of Buenos Aires province to Mar del Plata 10% of sighted groups were composed of mothers and calves (Coscarella, unpublish data). In Bahía Anegada, the majority of recorded sightings have been mother-calf pairs and adult individuals near the coast during spring-summer, also suggesting a recurrent breeding area (Bordino et al., 1999). For the Río Negro estuary, a total of 10 calves were recorded from January 2002 to December 2011 (Failla et al., 2012).
Sub-criterion C2: Feeding Areas
This IMMA’s oceanographic conditions promote high levels of productivity and marine diversity, providing an ample prey base for marine mammals. The fish assemblage of the IMMA (locally called variado costero) is composed of circa 30 species of bony, cartilaginous fish and small squids, with a persistent occurrence in time and specific composition. Biologically, it is defined as a demersal fish association that gives rise to a multi-species fishery, both artisanal and industrial. The distribution area of this association of species ranges from the coastline to 50 m isobath, extending from 34°S northern limit (Chuy, Uruguay) to 41°S, southern limit of the Province of Buenos Aires, although some species have a wider distribution. All the marine mammal species in this IMMA prey on the same assemblage, with the addition of the northern anchovy (Engraulis anchoita) stock that inhabits mid shelf (depths of 30-90m; north of 41ºS) and it is currently considered underexploited (Buratti et al., 2020; Ciancio et al. 2020).
Species feeding on this assemblage include the resident Lahille´s bottlenose and franciscana dolphins. It has been suggested that local movements of Lahille´s bottlenose dolphins to the Rio Negro estuarine areas are related to prey occurrence (Vermeulen et al., 2017). Stable isotope analysis of carbon (δ13C) and nitrogen (δ15N) from bone samples of Lahille’s bottlenose dolphins showed historical differences in foraging ecology between animals from Argentina and those of Uruguay and Brazil. Their considerably broad isotopic niche was maintained over decades, with a high proportion of demersal prey, mainly from coastal marine waters. Lahille´s bottlenose dolphins from Argentina and Uruguay showed a total isotopic niche segregation in the last 40 years, probably reflecting a spatial/ecological structuring in this region (Campos Rengel et al., 2021).
Franciscana prey on circa 20 fish, 2 squid of the variado costero and 4 crustacean species in the area, most of them juvenile stages of commercially targeted species (Rodríguez et al 2002; Paso Viola et al., 2014). The differences in their diet suggest at least three different foraging habitats, including estuarine and two main marine areas. Across this area, franciscanas have diets with different protein energy and water mass compositions, but similar protein-to-lipid energy ratios. These results suggest that the different estuarine and marine habitats are associated with different prey composition niches, but similar realised nutritional niches (Denuncio et al.,2017).
Stomach content and isotopic analyses of Common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in this IMMA indicate that they prey mainly on pelagic schooling fish and squid, with the Argentine anchovy as the main prey and a high diversity of small pelagic fishes and squids (Romero et al., 2012; Saporiti et al.,2015; Loizaga de Castro et al., 2016).
South American sea lions (Oatria byronia) and fur seals (Arctocephalus australis), are considered as dietary generalists that opportunistically feed on several prey species found in this IMMA (Naya et al., 2002; Suarez et al., 2005) while showing a horizontal overlap in foraging areas (Gonzalez Carman et al., 2016). Diet analysis showed that sea lions prefer demersal species (Franco-Trecu et al., 2014; Frau-Martinez, 2009; Szteren et al., 2004, 2018) while fur seals mostly consume pelagic prey (Drago et al., 2017; Franco-Trecu et al., 2014; Szteren et al., 2018; Vales et al., 2014; Machado et al., 2020), suggesting a potential dietary niche segregation. The sea lions consume at least 12 species, while for the fur seals´ diet includes ten species, sharing 4 prey species (2 demersal and 2 pelagic), all of them part of the variado costero and anchovies. Nutritional niche analysis reports that both species exhibit a high prey composition niche overlap, demonstrating that they consumed different prey species but with similar macronutrient composition ranges (Denuncio et al., 2021).
The La Plata River estuary and the nearby coastal marine area is a foraging habitat for lactating South American sea lion females that breed in the island complex of Isla de Lobos (Uruguay), as they regularly perform foraging trips to the proposed IMMA (Rodríguez et al., 2013). During the autumn–winter period, sea lions, fur seals, Green (Chelonia mydas), Loggerhead (Caretta caretta) and Leatherback turtles (Dermochelys coriacea), as well as Black-browed albatrosses (Thalassarche melanophris), regularly forage in the continental shelves of Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil, mainly over the Argentine Exclusive Economic Zone and the Argentina-Uruguay Common Fishing Zone. All these megafaunal species share waters shallower than 50 m in the Río de la Plata as the habitat with the highest suitability (Rodríguez et al., 2013; Gonzalez Carman et al., 2016; Annex, Fig.5).
Sub-criterion C3: Migration Routes
C3a – Whale Seasonal Migratory Route
C3b – Migration / Movement Area
Southern right whales concentrate off the SW Atlantic in two main reproductive areas (Península Valdés-Argentina and Santa Catarina-Brazil). Sightings of this species in intermediate areas, such as Southern Brazil, Uruguay and northern Argentina have increased since the 1990s (IWC, 2013) with sightings occurring between July and September, a period correlating to the northward migration from high latitude feeding grounds. During this time they are typically observed at depths of up to 50 m and demonstrate short residency times typical of migratory stopovers (###lt## 7 days). The species is also observed in areas beyond the 200m contour line between October and December, a period corresponding to the southward return migration from low latitude breeding grounds to high latitude feeding grounds (Mandiola et al.,2020).
Criterion D – Special Attributes
Sub-criterion D1 – Distinctiveness
Different genetic and morphological data for the Franciscana dolphin have indicated that there is population structuring throughout its range, leading to the designation of new subdivisions within each Franciscana Management Area (FMA) (Cunha et al. 2014). Within FMA IV, the region that includes Argentina’s coastline, five regions have been identified, each with high levels of genetic differentiation (Gariboldi et al. 2015; 2016):
- Samborombón Oeste / Samborombón Sur (FMAa)
- Cabo San Antonio / Buenos Aires Este (FMAb)
- Necochea / Claromecó / Buenos Aires Suroeste (FMAc)
- Monte Hermoso (FMAd)
- Río Negro (FMAe).
In 2023 the International Whaling Commission recognized these new subdivisions for the FMAIV. Of particular importance for the definition of this IMMA, is the genetic differences found between the Bahía Samborombon genetic unit (FMA IV-a; Gariboldi et al., 2015; 2016) and Uruguay (FMA III; Costa Urrutia et al., 2012). Although the La Plata River estuary is an environmental continuum between the coasts of Uruguay and Argentina, this micro-geographic differentiation supports the separation of franciscanas found in this IMMA and those occurring in Southern Brazil and Uruguay coastal ecosystem.
Sub-criterion D2 – Diversity
The IMMA is characterised by year-round residence of Lahille’s bottlenose dolphins and the Franciscanas, which are the two most endangered species of small cetaceans in the Southwest Atlantic. Other sympatric species are included under the IMMA criteria including south American sea lions, South American fur seals, southern right whales and common dolphins.
Additional species that are regularly recorded in the IMMA include killer whales (Orcinus orca), dusky dolphins (Aethalodelphis obscurus), southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina), and Burmeister’s porpoises (Phocoena spinipinnis) and humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) (Bastida & Rodríguez, 2003).
Supporting Information
Acha, E. M., Mianzan, H., Guerrero, R., Carreto, J., Giberto, D., Montoya, N., & Carignan, M. (2008). An overview of physical and ecological processes in the Rio de la Plata Estuary. Continental shelf research, 28(13), 1579-1588.
Bastida, R., & Rodríguez, D. (1994). Hallazgo de un apostadero estacional de lobos marinos de dos pelos, Arctocephalus australis (Zimmerman, 1783), en bajos fondos frente a la costa de Mar del Plata (Provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina). Anales de la Cuarta Reunión de Trabajo de Especialistas en Mamíferos Acuáticos de América del Sur . Centro de Investigación y Manejo de Mamíferos Marinos, CONICYT, Santiago de Chile, 1-22.
Bastida, R., & Rodríguez, D. (2003). Mamíferos Marinos de Patagonia y Antártida. 1ra. Ed. Buenos Aires. Vázquez Maziini Editores.
Bordino, P., Thompson, G., & Iñiguez, M. (1999). Ecology and behaviour of the franciscana (Pontoporia blainvillei) in Bahía Anegada, Argentina. Journal of Cetacean Research and Management, 1(2), 213-222.
Bordino, P., Thompson, G., & Iñiguez, M. (1999). Ecology and behaviour of the franciscana (Pontoporia blainvillei) in Bahía Anegada, Argentina. Journal of Cetacean Research and Management, 1(2), 213-222.
Buratti, C., Díaz de Astarloa, J., Hüne, M., Irigoyen, A., Landaeta, M., Riestra, C., Vieira, J.P. & Di Dario, F. (2020). Engraulis anchoita. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T195023A159405500.
Campos-Rangel, A., Bastida, R., Fruet, P., Laporta, P., Cappozzo, H. L., Valdivia, M., … & Botta, S. (2021). Historic foraging ecology of the endangered Lahille’s bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus gephyreus) inferred by stable isotopes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 258, 107393.
Castello, H., Bastida, R., Montes, G. and Palermo, G. (1983). La tonina. Fauna Argentina 18: 1-32. Centro Editor de América Latina. Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Ciancio, J.E., Bartes, S., Fernández, S., Harillo, C. and Lancelotti, J. 2020. Energy density predictors for Argentine Anchovy (Engraulis anchoita), a key species of the South Western Atlantic Ocean. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 149(2): 204-212.
Coscarella, M. A., Dans, S. L., Degrati, M., Garaffo, G. V., & Crespo, E. A. (2012). Bottlenose dolphins at the southern extreme of the south-western Atlantic: local population decline?. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 92(8), 1843-1849.
Costa, P., M.Piedra, P.Franco, E. Paez (2007). Distribution and habitat use patterns of southern right whales, Eubalaena australis, off Uruguay. Journal of Cetacean Research and Management, 9(1), 45.
Costa-Urrutia, P., Abud, C., Secchi, E. R., & Lessa, E. P. (2012). Population genetic structure and social kin associations of franciscana dolphin, Pontoporia blainvillei. Journal of Heredity, 103(1), 92-102.
Crespo, E. A., Coscarella, M., Arias, M., & Sueyro, N. (2020). Abundance estimation of franciscana dolphins by means of aerial surveys in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Working Paper presented to the 2020 IWC-SC.
Cunha, H. A., Medeiros, B. V., Barbosa, L. A., Cremer, M. J., Marigo, J., Lailson-Brito, J., … & Solé-Cava, A. M. (2014). Population structure of the endangered franciscana dolphin (Pontoporia blainvillei): reassessing management units. PloS one, 9(1), e85633.
Danilewicz, D., Moreno, I. B., Tavares, M., & Sucunza, F. (2017). Southern right whales (Eubalaena australis) off Torres, Brazil: group characteristics, movements, and insights into the role of the Brazilian-Uruguayan wintering ground. Mammalia, 81(3), 225-234.
Dassis, M., Farenga, M., Bastida, R., & Rodríguez, D. (2012). At-sea behavior of South American fur seals: Influence of coastal hydrographic conditions and physiological implication. Mammalian Biology, 77(1), 47-52.
Dassis, M., Farenga, M., Bastida, R., & Rodríguez, D. (2012). At-sea behavior of South American fur seals: Influence of coastal hydrographic conditions and physiological implication. Mammalian Biology, 77(1), 47-52.
Denuncio, P. E., Bastida, R. O., Danilewicz, D., Morón, S., Rodríguez-Heredia, S., & Rodríguez, D. H. (2013). Calf chronology of the franciscana dolphin (Pontoporia blainvillei): birth, onset of feeding, and duration of lactation in coastal waters of Argentina. Aquatic Mammals, 39(1), 73.
Denuncio, P. E., Bastida, R. O., Danilewicz, D., Morón, S., Rodríguez-Heredia, S., & Rodríguez, D. H. (2013). Calf chronology of the franciscana dolphin (Pontoporia blainvillei): birth, onset of feeding, and duration of lactation in coastal waters of Argentina. Aquatic Mammals, 39(1), 73-78.
Denuncio, P., Gana, J. C., Giardino, G. V., Rodríguez, D. H., & Machovsky-Capuska, G. E. (2021). Prey composition and nutritional strategies in two sympatric pinnipeds. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 545, 151629.
Denuncio, P., Gana, J. C., Giardino, G. V., Rodríguez, D. H., & Machovsky-Capuska, G. E. (2021). Prey composition and nutritional strategies in two sympatric pinnipeds. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 545, 151629.
Denuncio, P., Viola, M. N. P., Machovsky-Capuska, G. E., Raubenheimer, D., Blasina, G., Machado, R., … & Rodriguez, D. H. (2017). Population variance in prey, diets and their macronutrient composition in an endangered marine predator, the Franciscana dolphin. Journal of sea research, 129, 70-79.
Denuncio, P.E., N.Paso Viola, I.Cáceres-Saez, H.L. Cappozzo, D.Rodríguez, M.A. Agustina (2019). Pontoporia blainvillei. En: SAyDS–SAREM (eds.) Categorización 2019 de los mamíferos de Argentina según su riesgo de extinción. Lista Roja de los mamíferos de Argentina. Versión digital: http://cma.sarem.org.ar.
Díaz de Astarloa, J. M., A. Aubone y M. B. Cousseau. (1999). Asociaciones ícticas de la plataforma costera de Uruguay y norte de Argentina, y su relación con los parámetros ambientales. Physis, Secc. A 57(132-133): 29-45.
Díaz de Astarloa, J. M., A. Aubone y M. B. Cousseau. 1999. Asociaciones ícticas de la plataforma costera de Uruguay y norte de Argentina, y su relación con los parámetros ambientales. Physis, Secc. A 57(132-133): 29-45.
Drago, M., Cardona, L., Franco‐Trecu, V., Crespo, E. A., Vales, D. G., Borella, F., … & Inchausti, P. (2017). Isotopic niche partitioning between two apex predators over time. Journal of Animal Ecology, 86(4), 766-780.
Failla, M., Seijas, V.A. and Vermeulen, E. 2016. Occurrence of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Río Negro Estuary, Argentina, and their mid-distance movements along the northeastern Patagonian coast. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Mammals 11(1-2): 170-177.
Franco-Trecu, V., Aurioles-Gamboa, D., & Inchausti, P. (2014). Individual trophic specialisation and niche segregation explain the contrasting population trends of two sympatric otariids. Marine Biology, 161(3), 609-618.
Frau-Martinez, M.R. (2009). Dieta del lobo fino (Arctocephalus australis) en Isla de Lobos (Maldonado- Uruguay) durante el período de reproducción. Tesis de Grado, Universidad de la República (Uruguay). Facultad de Ciencias
Fruet, P. F., Secchi, E. R., Daura-Jorge, F., Vermeulen, E., Flores, P. A., Simoes-Lopes, P. C., … & Möller, L. M. (2014). Remarkably low genetic diversity and strong population structure in common bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from coastal waters of the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Conservation Genetics, 15(4), 879-895.
Gariboldi, M. C., Túnez, J. I., Dejean, C. B., Failla, M., Vitullo, A. D., Negri, M. F., & Cappozzo, H. L. (2015). Population genetics of Franciscana dolphins (Pontoporia blainvillei): introducing a new population from the southern edge of their distribution. PLoS One, 10(7), e0132854.
Gariboldi, M. C., Túnez, J. I., Failla, M., Hevia, M., Panebianco, M. V., Paso Viola, M. N., … & Cappozzo, H. L. (2016). Patterns of population structure at microsatellite and mitochondrial DNA markers in the franciscana dolphin (Pontoporia blainvillei). Ecology and evolution, 6(24), 8764-8776.
Giardino, G. V., Mandiola, M. A., Bastida, J., Denuncio, P. E., Bastida, R. O., & Rodríguez, D. H. (2016). Travel for sex: Long-range breeding dispersal and winter haulout fidelity in southern sea lion males. Mammalian Biology, 81(1), 89-95.
Giardino, G., Bastida, J., Mandiola, M. A., Bastida, R., & Rodríguez, D. (2017). Estimated population size of two South American sea lion male haulouts from the northern coast of Argentina. Mammalia, 81(2), 197-202
González Carman, V., Mandiola, A., Alemany, D., Dassis, M., Seco Pon, J. P., Prosdocimi, L., … & Copello, S. (2016). Distribution of megafaunal species in the Southwestern Atlantic: key ecological areas and opportunities for marine conservation. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 73(6), 1579-1588.
Groch, K. R., Palazzo Jr, J. T., Flores, P. A. C., Adler, F. R., & Fabian, M. E. (2005). Recent rapid increases in the right whale (Eubalaena australis) population off southern Brazil. Latin American journal of aquatic mammals, 41-47.
Hevia, M, Iñíguez Bessega, M.A., Reyes Reyes, M.V., Zuazquita, E.P.(2022). A review of marine protected areas in Argentina and their overlap with current cetacean distribution. A Report prepared for OceanCare. May 2022. 83p.
IWC. 2018. Report of the 67b International Whaling Commission Scientific Committee. Journal of Cetacean Research & Management 18 (Suppl):66-67.
IWC. 2013. Report of the IWC Workshop on the Assessment of Southern Right Whales. J. Cetacean Res. Manage. (Suppl.) 14: 437-62.
Lodi, L., Domit, C., Laporta, P., Di Tullio, J. C., Martins, C. C., & Vermeulen, E. (2016). Report of the Working Group on the Distribution of Tursiops truncatus in the Southwest Atlantic Ocean. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Mammals, 11(1-2), 29-46.
Loizaga de Castro, R., Saporiti, F., Vales, D. G., García, N. A., Cardona, L., & Crespo, E. A. (2016). What are you eating? A stable isotope insight into the trophic ecology of short-beaked common dolphins in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Mammalian Biology, 81(6), 571-578.
Lucas, A. J., Guerrero, R. A., Mianzan, H. W., Acha, E. M., & Lasta, C. A. (2005). Coastal oceanographic regimes of the northern Argentine continental shelf (34–43 S). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 65(3), 405-420.
Machado, R., de Oliveira, L. R., Ott, P. H., Haimovici, M., Cardoso, L. G., Milmann, L., … & Borges-Martins, M. (2020). Trophic overlap between marine mammals and fisheries in subtropical waters in the western South Atlantic. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 639, 215-232.
Macchi, G. J., & Acha, E. M. (1998). Aspectos reproductivos de las principales especies de peces en la Zona Común de Pesca Argentino-Uruguaya y en El Rincón. Noviembre, 1994. INIDEP informe técnico, 21. p. 67-89.
Mandiola, M. A., Giardino, G. V., Bastida, J., Rodríguez, D. H., & Bastida, R. O. (2015). Marine mammal occurrence in deep waters of the Brazil-Malvinas Confluence off Argentina during summer. Mastozoología neotropical, 22(2), 397-402.
Mandiola, M. A., Giardino, G., Bastida, J., Morón, S., Rodríguez, D. H., & Bastida, R. (2020). Half a century of sightings data of southern right whales in Mar del Plata (Buenos Aires, Argentina). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 100(1), 165-171.
Mandiola, M.A. (2015). Evaluación de la presencia de lobos marinos de dos pelos Sudamericanos (Arctocephalus australis) en la Provincia de Buenos Aires, y sus interacciones con pesquerías de la región. Tesis de Doctorado en Ciencias Biológicas, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Mar del Plata, Argentina.
Mandiola, M.A. (2015). Evaluación de la presencia de lobos marinos de dos pelos Sudamericanos (Arctocephalus australis) en la Provincia de Buenos Aires, y sus interacciones con pesquerías de la región. Tesis de Doctorado en Ciencias, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Mar del Plata.
Mendez, M., Rosenbaum, H. C., Subramaniam, A., Yackulic, C., & Bordino, P. (2010). Isolation by environmental distance in mobile marine species: molecular ecology of franciscana dolphins at their southern range. Molecular ecology, 19(11), 2212-2228
Mianzan, H., Lasta, C., Acha, E., Guerrero, R., Macchi, G., & Bremec, C. (2001). The Río de la Plata estuary, Argentina-Uruguay. In Coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America (pp. 185-204). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Negri, M. F., Denuncio, P., Panebianco, M. V., & Cappozzo, H. L. (2012). Bycatch of franciscana dolphins Pontoporia blainvillei and the dynamic of artisanal fisheries in the species’ southernmost area of distribution. Brazilian Journal of oceanography, 60, 149-158.
Ott P.H., Di Tullio J., Prado J., Danilewicz, D., Passadore C., Failla M., Iñíguez Bessega M. and D.Rodríguez (2022). Marine Protected Areas: Their potential for the conservation of the species. Chapter 18. The Franciscana book, on the edge of survival. Simoes-Lopes and Cremer (Eds.). Elsevier y Academic Press. 424-464.
Paso-Viola, M. N., Denuncio, P., Negri, M. F., Rodríguez, D., Bastida, R., & Cappozzo, H. L. (2014). Diet composition of franciscana dolphin Pontoporia blainvillei from southern Buenos Aires, Argentina and its interaction with fisheries. Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía, 49(2), 393-400.
Perillo, G. M. E., Piccolo, M. C., Parodi, E., & Freije, R. H. (2001). The Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. In Coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America (pp. 205-217). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Perillo, G. M., & Piccolo, M. (1999). Geomorphological and physical characteristics of the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. In Estuaries of South America (pp. 195-216). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Petracci, P., Marbán, L., Sotelo, M., Massola, V., Valese, N., Zuazquita, E & Iñíguez Bessega, M. 2023. Occurrence of Lahille’s Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus ssp. gephyreus) in Bahía Blanca Estuary (Buenos Aires, Argentina). Preliminary information. Paper submitted to the 69A meeting of the International Whaling Commission Scientific Committee (SC/69A/SM/04). Bled, Slovenia, 24 April – 6 May. 11pp.
Rodríguez, D. H., Dassis, M., de Leon, A. P., Barreiro, C., Farenga, M., Bastida, R. O., & Davis, R. W. (2013). Foraging strategies of southern sea lion females in the La Plata River Estuary (Argentina–Uruguay). Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 88, 120-130.
Rodríguez, D. H., Giardino, G. V., Mandiola, M. A., Gana, J., León, M. C. D., Bastida, J., … & Bastida, R. O. (2021). Responding to human influence: southern sea lion males adapt to harbor habitats. In Ethology and Behavioral Ecology of Otariids and the Odobenid (pp. 415-435). Springer, Cham.
Rodriguez, D., Rivero, L., Bastida, R., 2002. Feeding ecology of the Franciscana (Pontoporia blainvillei) in estuarine and marine waters of northern Argentina. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Mamm. 1 (1), 77–94.
Romero, M. A., Dans, S. L., García, N., Svendsen, G. M., González, R., & Crespo, E. A. (2012). Feeding habits of two sympatric dolphin species off North Patagonia, Argentina. Marine Mammal Science, 28(2), 364-377.
Saporiti, F., Bearhop, S., Vales, D. G., Silva, L., Zenteno, L., Tavares, M., … & Cardona, L. (2015). Latitudinal changes in the structure of marine food webs in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 538, 23-34.
Szteren, D., Naya, D. E., & Arim, M. (2004). Overlap between pinniped summer diet and artisanal fishery catches in Uruguay. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Mammals, 119-125.
Szteren, D., Aurioles-Gamboa, D., Labrada-Martagón, V., Hernández-Camacho, C. J., & De María, M. (2018). Historical age-class diet changes in South American fur seals and sea lions in Uruguay. Marine Biology, 165(4), 1-17.
Vales, D. G., Saporiti, F., Cardona, L., De Oliveira, L. R., Dos Santos, R. A., Secchi, E. R., … & Crespo, E. A. (2014). Intensive fishing has not forced dietary change in the South American fur seal Arctophoca (= Arctocephalus) australis off Río de la Plata and adjoining areas. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 24(6), 745-759.
Vermeulen, E., & Bräger, S. (2015). Demographics of the disappearing bottlenose dolphin in Argentina: a common species on its way out?. PLoS One, 10(3), e0119182.
Vermeulen, E., Balbiano, A., Belenguer, F., Colombil, D., Failla, M., Intrieri, E., & Bräger, S. (2017). Site‐fidelity and movement patterns of bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in central Argentina: essential information for effective conservation. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 27(1), 282-292.
Vermeulen, E., Bastida, R., Berninsone, L. G., Bordino, P., Failla, M., Fruet, P., … & Bräger, S. (2017). A review on the distribution, abundance, residency, survival and population structure of coastal bottlenose dolphins in Argentina. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Mammals, 12(1-2), 2-16.
Vermeulen, E., Fruet, P., Costa, A., Coscarella, M. & Laporta, P. 2019. Tursiops truncatus ssp. gephyreus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T134822416A135190824. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T134822416A135190824.en.
Vermeulen,E., M. Failla, R.Loizaga de Castro, Romero, M.A., G.Svendsen, M.Coscarella, I.Cáceres-Saez, R.Bastida, M.Dassis (2019). Tursiops truncatus. En: SAyDS–SAREM (eds.) Categorización 2019 de los mamíferos de Argentina según su riesgo de extinción. Lista Roja de los mamíferos de Argentina. Versión digital: http://cma.sarem.org.ar.
Viñas, M. D., Marrari, M.Di Mauro, R. Cepeda, G. D., & Padovani, L. N. (2013). El zooplancton del hábitat reproductivo de la población bonaerense de anchoíta (Engraulis anchoita), con especial énfasis en crustáceos. Revista de Investigación y Desarrollo Pesquero, 23, p. 125-144
Wells, R. S., Cremer, M. J., Berninsone, L. G., Albareda, D., Wilkinson, K. A., Stamper, M. A., … & Bordino, P. (2022). Tagging, ranging patterns, and behavior of franciscana dolphins (Pontoporia blainvillei) off Argentina and Brazil: Considerations for conservation. Marine Mammal Science, 38(2), 571-605.
Zerbini, A.N., Secchi, E., Crespo, E., Danilewicz, D. & Reeves, R. 2017. Pontoporia blainvillei (errata version published in 2018). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T17978A123792204. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T17978A50371075.en.
Downloads
Download the full account of the Marine mammal coastal corridor in northern Argentina IMMA using the Brochure button below:
To make a request to download the GIS Layer (shapefile and/or geojson) for the Marine mammal coastal corridor in northern Argentina IMMA please complete the following Contact Form: