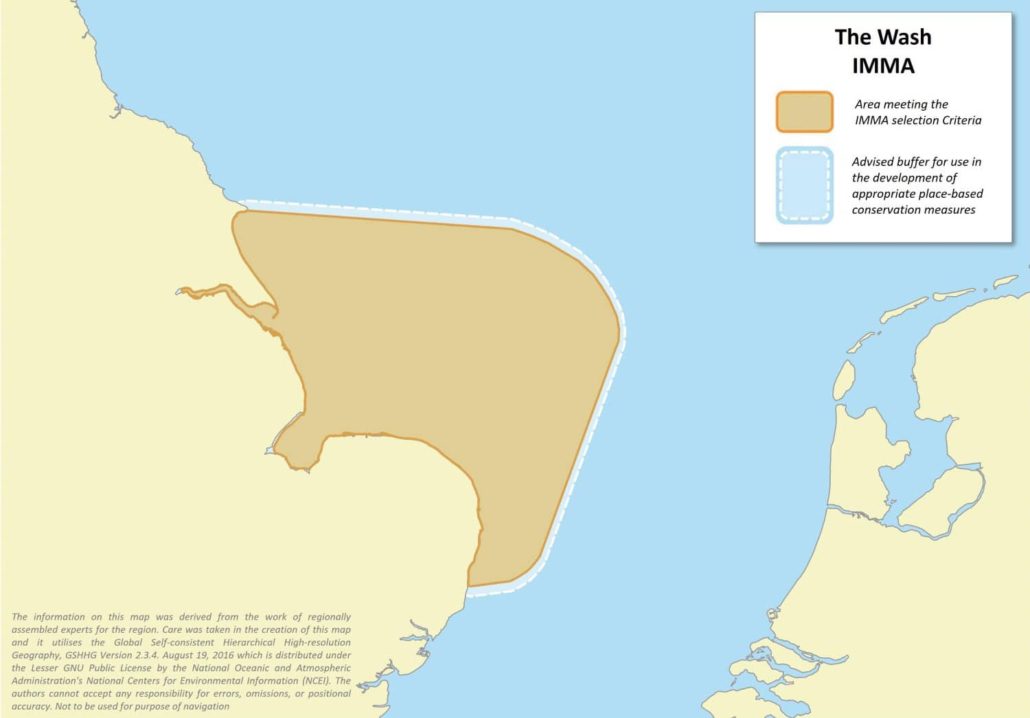
The Wash IMMA
Size in Square Kilometres
25,740 km2
Qualifying Species and Criteria
Harbour seal – Phoca vitulina
Criterion B (2), C (1,2)
Download fact sheet
Summary
This IMMA, which encompasses The Wash and North Norfolk Coast Special Area of Conservation, includes the haulout, breeding and foraging area of the majority of the English subpopulation of Atlantic harbour seals (Phoca vitulina vitulina). Harbour seals are coastal compared to the sympatric grey seal (Halichoerus grypus), and in this area they focus their foraging activities on sand banks at depths shallower than 30m. The population in this area has declined by around 25% in the last five years for unknown reasons.
Description of Qualifying Criteria
Criterion B: Distribution and Abundance
Sub-criterion B2: Aggregations
The IMMA provides habitat that supports around 4,250 Atlantic harbour seals (Phoca vitulina vitulina) (6,0000 until recently) (SCOS, 2022). This is the majority (>90%) of harbour seals in England and also represents 5% of the Northeast Atlantic harbour seals, and around 2.5% of the entire subspecies (Russell et al. 2022). Harbour seals in The Wash suffered huge population reductions of 50% in 1988 and 30% in 2002 due to outbreaks of Phocine Distemper Virus (PDV) (SCOS 2022). The population recovered following these events, but over the last five years numbers have again declined by around 25% between 2018 and 2022 according to both number of seals recorded during moult counts (Thompson and Russell 2022) and number of pups counted during breeding surveys (Thompson 2022). The reasons for these declines are unknown. This is a key subpopulation as it represents almost the entirety of the United Kingdom’s (UK) part of the Southern European harbour seal metapopulation (harbour seals elsewhere in the UK form a separate Scottish metapopulation; Carroll et al. (2020)). The habitat is also changing as a result of wind farm development.
Criterion C: Key Life Cycle Activities
Sub-criterion C1: Reproductive Areas
The harbour seals are resident in the area, breeding on the tidal sandbanks. A total of 1140 pups were counted in the most recent breeding survey in 2020, but this was 24% lower than the preceding survey in 2018 (SCOS, 2022).
Sub-criterion C2: Feeding Areas
The Wash is a very shallow (<30m) and productive area which incorporates the vast majority of foraging areas for the harbour seals that haul-out in The Wash (Carter et al. 2022). High at-sea density areas for harbour seals are usually adjacent to relatively large centres of abundance on land (i.e. haulout and breeding sites) and The Wash and surrounding waters is one of the areas most densely used for foraging in the UK. Harbour seal distribution is more tightly concentrated in coastal and inshore waters compared to sympatric grey seals (Halichoerus grypus), but with fine-scale structuring of density around the coast (Carter et al. 2022).
Supporting Information
Carroll, E. L., Hall, A., Olsen, M. T., Onoufriou, A. B., Gaggiotti, O. E., and Russell,D. J. F. (2020). Perturbation Drives Changing Metapopulation Dynamics in a Top Marine Predator. Proc.R.SocB. 287, 20200318.
Carter, M. I. D., Boehme, L., Cronin, M. A., Duck, C. D., Grecian, W. J., Hastie, G. D., Jessopp, M., Matthiopoulos, J., Mcconnell, B. J., Miller, D. L., Morris, C. D., Moss, S. E. W., Thompson, D., Thompson, P. M., & Russell, D. J. F. 2022. Sympatric seals, satellite tracking and protected areas: habitat-based distribution estimates for conservation and management. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9, 875869.
Thompson D. (2022) Preliminary report on the distribution and abundance of harbou seals (Phoca vitulina) during the 2022 breeding season in The Wash. SCOS Briefing Paper.
Thompson D. and Russell D.J.F. (2022) Recent changes in the status of harbour seals in the Wash and North Norfolk SAC and adjacent sites. SCOS Briefing Paper.
Russell D.J.F., Duck, C.D., Morris C.D., Riddoch N.G., Thompson D. (2022) Trends in seal abundance and grey seal pup production. SCOS Briefing Paper.
Wilson, L.J. and Hammond, P.S. 2019. The diet of harbour and grey seals around Britain: Examining the role of prey as a potential cause of harbour seal declines. Aquatic Conservation: Marine Freshwater Ecosystems, 29(S1): 71– 85.
Downloads
Download the full account of the The Wash IMMA using the Fact Sheet button below:
To make a request to download the GIS Layer (shapefile) for the The Wash IMMA please complete the following Contact Form: